Navigating The Shifting Sands Of Time: A Comprehensive Guide To Daylight Saving Time
Navigating the Shifting Sands of Time: A Comprehensive Guide to Daylight Saving Time
Related Articles: Navigating the Shifting Sands of Time: A Comprehensive Guide to Daylight Saving Time
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Shifting Sands of Time: A Comprehensive Guide to Daylight Saving Time. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Shifting Sands of Time: A Comprehensive Guide to Daylight Saving Time
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Shifting Sands of Time: A Comprehensive Guide to Daylight Saving Time
- 3.1 A Historical Journey: From Efficiency to Energy Savings
- 3.2 The Global Landscape: A Patchwork of Practices
- 3.3 The Shifting Sands of Debate: Arguments for and Against DST
- 3.4 Navigating the Complexities: Understanding the Implementation and Impact of DST
- 3.5 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about DST
- 3.6 Tips for Managing DST: Minimizing Disruption and Maximizing Benefits
- 3.7 Conclusion: A Complex Issue with No Easy Answers
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Shifting Sands of Time: A Comprehensive Guide to Daylight Saving Time
Daylight Saving Time (DST), the practice of adjusting clocks forward by an hour during warmer months, is a phenomenon that has captivated societies worldwide for over a century. While its implementation and impact vary across countries and regions, its fundamental purpose remains consistent: to maximize daylight hours during the summer months, offering potential benefits for both energy consumption and public safety. This article delves into the intricacies of DST, exploring its history, rationale, implementation, and ongoing debate.
A Historical Journey: From Efficiency to Energy Savings
The concept of adjusting clocks to align with daylight hours dates back centuries, with notable proponents including Benjamin Franklin in the 18th century. However, it was during World War I that DST gained widespread adoption as a means to conserve energy during wartime shortages. The idea was simple: by shifting clocks forward, people could utilize natural daylight for longer periods, reducing reliance on artificial lighting and, consequently, energy consumption.
The United States first implemented DST in 1918, but the practice was repealed shortly after the war. It was revived during World War II and later reintroduced in 1966, becoming a regular practice in the country. While energy conservation remains a key argument for DST, its proponents also point to other benefits such as increased public safety, economic activity, and recreational opportunities during longer daylight hours.
The Global Landscape: A Patchwork of Practices
While the United States remains a staunch advocate for DST, its implementation varies significantly across the globe. Some countries, like China and Japan, do not observe DST at all, while others adopt different variations of the practice. The European Union, for instance, implemented standardized DST rules in 1980, but these were abolished in 2019, leaving individual member states to decide their own policies.
This global patchwork of DST practices highlights the complex interplay of cultural, economic, and political factors that influence its adoption. While some regions find it beneficial for various reasons, others view it as disruptive and unnecessary, arguing that its purported benefits are often outweighed by negative consequences.
The Shifting Sands of Debate: Arguments for and Against DST
The debate surrounding DST is multifaceted and often heated, with proponents and opponents presenting compelling arguments.
Arguments in favor of DST:
- Energy Conservation: By extending daylight hours, DST allows people to utilize natural sunlight for longer periods, potentially reducing the need for artificial lighting and contributing to energy savings.
- Public Safety: Longer daylight hours can enhance visibility and reduce the risk of accidents, particularly during evening commutes.
- Economic Benefits: Extended daylight hours can boost retail activity, outdoor recreation, and other businesses that rely on daylight.
- Improved Health and Well-being: Studies suggest that increased exposure to sunlight can have positive effects on mood, sleep patterns, and overall health.
Arguments against DST:
- Disruption of Sleep Patterns: The abrupt shift in clock time can disrupt natural sleep cycles, leading to fatigue, reduced productivity, and increased health risks.
- Negative Impact on Health: Some studies suggest a correlation between DST and increased heart attacks, strokes, and other health issues.
- Inconsistency and Confusion: The practice of shifting clocks twice a year can cause confusion and inconvenience, particularly for individuals who travel across time zones or work in industries with strict scheduling.
- Limited Energy Savings: The actual energy savings attributed to DST are often debated, with some studies suggesting minimal or even negative impacts on energy consumption.
Navigating the Complexities: Understanding the Implementation and Impact of DST
Understanding the implementation and impact of DST requires considering various factors:
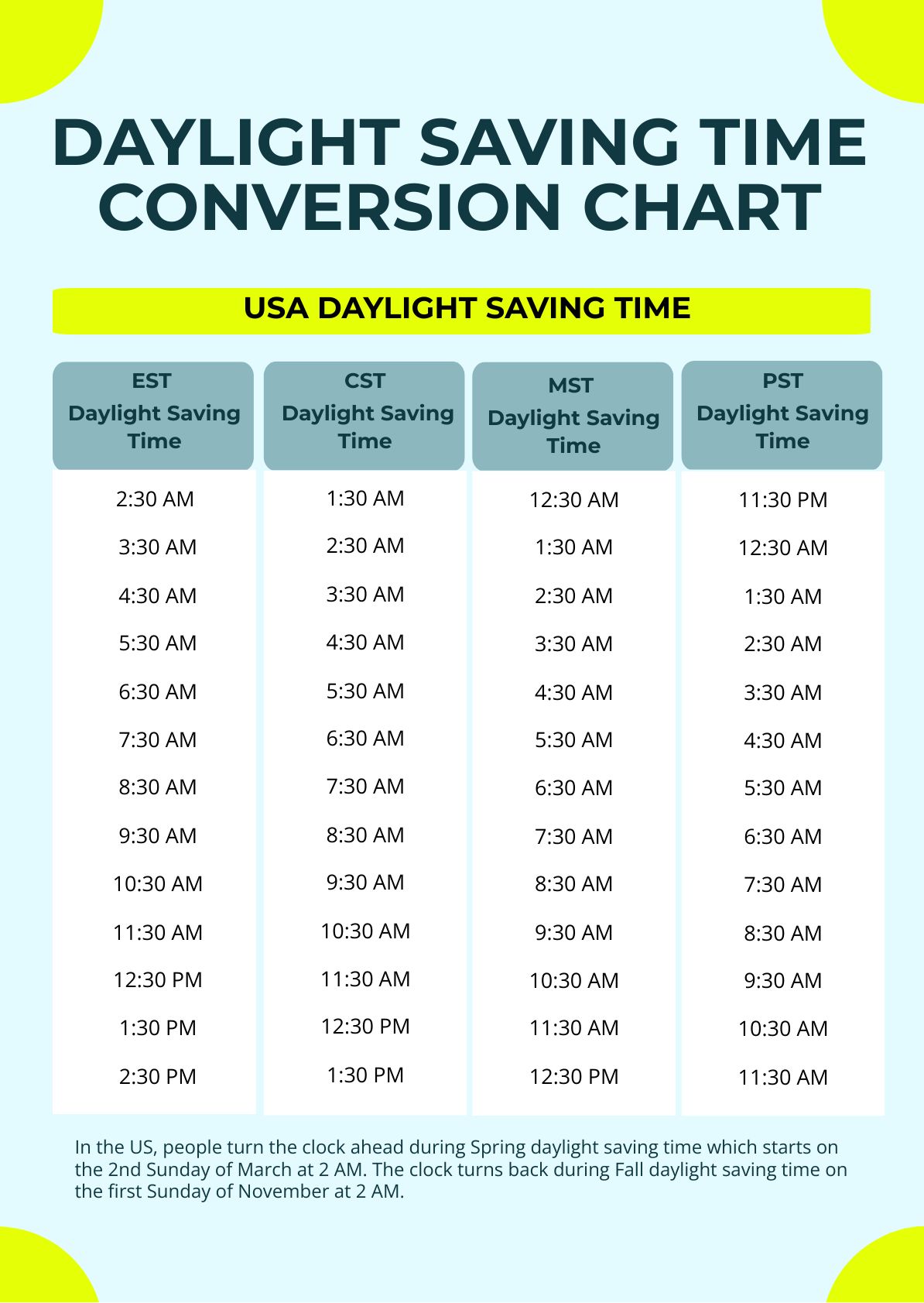
- Duration of DST: The duration of DST varies across countries and regions. In the United States, for example, it typically lasts from the second Sunday in March to the first Sunday in November.
- Time Zone Differences: DST implementation can vary across different time zones within a country. This can lead to complexities for individuals who travel or work across time zones.
- Economic and Social Impacts: The impact of DST on economic activity, public safety, and overall well-being is a subject of ongoing research and debate.
- Environmental Considerations: The environmental impact of DST, particularly in terms of energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions, remains a contentious issue.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about DST
1. When does Daylight Saving Time begin and end?
The start and end dates of DST vary by country and region. In the United States, it typically begins on the second Sunday in March and ends on the first Sunday in November.
2. Why do we observe Daylight Saving Time?
The primary rationale behind DST is to maximize daylight hours during the summer months, potentially leading to energy savings, increased public safety, and economic benefits.
3. What are the benefits of Daylight Saving Time?
Proponents of DST argue that it leads to energy savings, improved public safety, increased economic activity, and enhanced health and well-being.
4. What are the drawbacks of Daylight Saving Time?
Critics of DST argue that it disrupts sleep patterns, negatively impacts health, creates inconsistency and confusion, and may not lead to significant energy savings.
5. Is Daylight Saving Time still used in the United States?
Yes, the United States currently observes DST from the second Sunday in March to the first Sunday in November.
6. Is Daylight Saving Time used globally?
No, DST is not universally observed. Some countries, such as China and Japan, do not observe DST at all. Other countries, like the European Union, have abolished standardized DST rules, leaving individual member states to decide their own policies.
7. What is the future of Daylight Saving Time?
The future of DST is uncertain. Some countries, including the United States, are currently considering legislation to abolish DST or make it permanent. The debate surrounding DST is likely to continue, with proponents and opponents presenting their arguments for and against the practice.
Tips for Managing DST: Minimizing Disruption and Maximizing Benefits
While the debate surrounding DST continues, individuals can take steps to minimize its disruptive effects and maximize its potential benefits:
- Gradually Adjust Sleep Schedule: In the weeks leading up to the shift, adjust your sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up 15 minutes earlier or later each day to ease the transition.
- Maintain Regular Sleep Routine: During DST, maintain a consistent sleep schedule, going to bed and waking up at approximately the same time each day to regulate your body clock.
- Limit Screen Time Before Bed: Avoid using electronic devices for at least an hour before bedtime, as the blue light emitted from screens can interfere with melatonin production and disrupt sleep.
- Prioritize Outdoor Activities: Take advantage of the extended daylight hours by engaging in outdoor activities, promoting physical activity, and maximizing exposure to natural sunlight.
- Stay Informed: Stay up-to-date on any changes or debates surrounding DST in your region to make informed decisions and adjust your lifestyle accordingly.
Conclusion: A Complex Issue with No Easy Answers
The debate surrounding Daylight Saving Time reflects a complex interplay of societal, economic, and environmental considerations. While proponents highlight its potential benefits in terms of energy savings, public safety, and economic activity, opponents argue that its disruptions to sleep patterns, health, and overall well-being outweigh any potential advantages. The future of DST remains uncertain, with ongoing debates and potential legislative changes shaping its trajectory in various countries and regions. Navigating this complex issue requires a balanced understanding of its arguments, its implementation, and its potential impact on individuals and society as a whole.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Shifting Sands of Time: A Comprehensive Guide to Daylight Saving Time. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!