Unveiling The Differences: A Comprehensive Guide To The Jewish And Gregorian Calendars
Unveiling the Differences: A Comprehensive Guide to the Jewish and Gregorian Calendars
Related Articles: Unveiling the Differences: A Comprehensive Guide to the Jewish and Gregorian Calendars
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Differences: A Comprehensive Guide to the Jewish and Gregorian Calendars. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Differences: A Comprehensive Guide to the Jewish and Gregorian Calendars
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Differences: A Comprehensive Guide to the Jewish and Gregorian Calendars
- 3.1 The Gregorian Calendar: A Solar System
- 3.2 The Jewish Calendar: A Lunar-Solar System
- 3.3 Key Differences: A Comparative Overview
- 3.4 Beyond the Basics: Understanding the Significance
- 3.5 FAQ: Addressing Common Questions
- 3.6 Tips for Navigating the Jewish Calendar
- 3.7 Conclusion: Bridging the Gap
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Differences: A Comprehensive Guide to the Jewish and Gregorian Calendars

The Gregorian calendar, the most widely used calendar system globally, governs our daily lives, dictating work schedules, holidays, and even the passage of time. However, a parallel system exists, the Jewish calendar, which holds immense cultural and religious significance for millions worldwide. Understanding the differences between these two calendars is crucial for appreciating the rich tapestry of cultural and religious practices that define our world.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the Jewish and Gregorian calendars, highlighting their unique characteristics and outlining their distinct approaches to timekeeping. By comparing these systems, we gain valuable insights into the diverse ways humans have structured their understanding of time and its impact on their lives.
The Gregorian Calendar: A Solar System
The Gregorian calendar, named after Pope Gregory XIII, is a solar calendar based on the Earth’s revolution around the sun. Its foundation lies in the concept of a year being the time it takes for the Earth to complete one orbit around the sun, approximately 365.2422 days. To accommodate the extra fraction of a day, the Gregorian calendar employs a leap year system, adding an extra day to February every four years, except for years divisible by 100 but not by 400.
This system ensures that the calendar remains aligned with the Earth’s position relative to the sun, preventing seasonal drift and maintaining the accuracy of equinoxes and solstices. The Gregorian calendar, with its 12 months and 365 days (or 366 in leap years), is a familiar framework for most of the world, governing our daily routines and societal structures.
The Jewish Calendar: A Lunar-Solar System
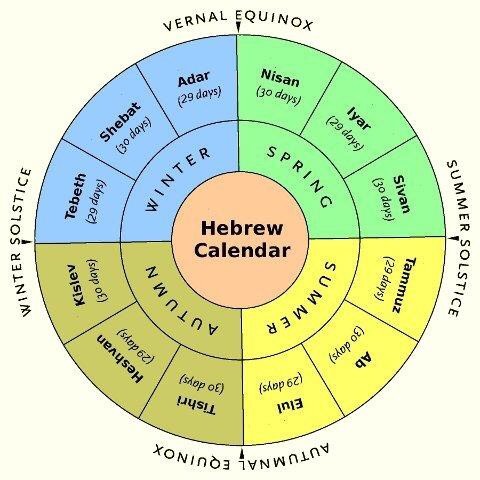
The Jewish calendar, rooted in Jewish tradition and religious practices, operates on a unique lunar-solar system. Unlike the Gregorian calendar, which primarily focuses on the Earth’s relationship with the sun, the Jewish calendar prioritizes the lunar cycle, with months determined by the phases of the moon. However, the Jewish calendar incorporates a solar component to ensure its alignment with the seasons and the celebration of agricultural festivals.
Each month in the Jewish calendar begins with the appearance of the new moon, with the length of each month varying between 29 and 30 days. To synchronize the calendar with the solar year, the Jewish calendar introduces a leap year system, adding an extra month every two or three years. This leap month, known as Adar II, ensures that Passover, a key agricultural festival, falls during the spring season.
Key Differences: A Comparative Overview
The fundamental difference between the Gregorian and Jewish calendars lies in their underlying principles. The Gregorian calendar is solar-based, prioritizing the Earth’s orbit around the sun. Conversely, the Jewish calendar is lunar-solar, primarily relying on the lunar cycle but incorporating solar elements to maintain seasonal alignment.
This difference manifests in several key aspects:
1. Length of the Year: The Gregorian calendar has a fixed length of 365 days, with an extra day added every four years (except for years divisible by 100 but not by 400). The Jewish calendar, however, has a variable length, ranging between 353 and 385 days, depending on the inclusion of a leap month.
2. Month Length: The Gregorian calendar has fixed month lengths, ranging from 28 to 31 days. The Jewish calendar, on the other hand, has variable month lengths, with each month starting with the appearance of the new moon, resulting in months ranging from 29 to 30 days.
3. Leap Years: The Gregorian calendar employs a leap year system based on the solar cycle, adding an extra day to February every four years. The Jewish calendar also has a leap year system, but it is based on a lunar-solar calculation, adding an extra month, Adar II, every two or three years to ensure Passover aligns with the spring season.
4. Calendar Start: The Gregorian calendar begins with January 1st, while the Jewish calendar begins with Tishrei 1st, which typically falls in September or October.
5. Weekday Start: The Gregorian calendar begins the week with Sunday, while the Jewish calendar begins the week with Saturday.
Beyond the Basics: Understanding the Significance
While the differences between the Gregorian and Jewish calendars may seem technical, they hold profound significance for the Jewish community. The Jewish calendar is not merely a system for tracking time; it is intricately interwoven with Jewish religious practice and cultural identity.
The lunar-solar system of the Jewish calendar ensures that key religious observances, such as Passover, Rosh Hashanah, and Yom Kippur, align with specific agricultural cycles and lunar phases. This connection between time, nature, and religious practice is deeply embedded in Jewish tradition and provides a framework for understanding the cyclical nature of life and the importance of observing religious rituals at specific times of the year.
Furthermore, the Jewish calendar’s unique system of leap years and month lengths reflects the importance of maintaining a balance between the lunar and solar cycles, ensuring that the calendar remains aligned with both the phases of the moon and the seasons. This delicate balance underscores the complex relationship between humanity, nature, and the passage of time, a theme that resonates throughout Jewish tradition and cultural practices.
FAQ: Addressing Common Questions
1. How do I convert a date from the Gregorian calendar to the Jewish calendar?
Online conversion tools are readily available, providing accurate conversions between the Gregorian and Jewish calendars. These tools consider the intricacies of both calendars, including leap years and month lengths, ensuring precise conversions.
2. How does the Jewish calendar impact daily life?
The Jewish calendar plays a significant role in shaping daily life for observant Jews. It dictates the timing of religious observances, such as Shabbat, holidays, and fast days, and influences dietary practices, particularly during Passover.
3. Can the Jewish calendar be used for non-religious purposes?
While the Jewish calendar is primarily used for religious purposes, it can be used for non-religious purposes as well. For example, it can be used to track the phases of the moon, calculate the dates of specific astronomical events, or simply to explore the history and culture of the Jewish calendar.
4. What are the challenges associated with the Jewish calendar?
The Jewish calendar’s lunar-solar system can lead to inconsistencies in the length of the year, with some years being shorter or longer than others. This can create challenges in scheduling events, particularly for those who observe both the Jewish and Gregorian calendars.
5. How has the Jewish calendar evolved over time?
The Jewish calendar has undergone several revisions throughout history. Early Jewish calendars were primarily lunar, with the inclusion of solar elements later to ensure alignment with the seasons. The current Jewish calendar, as we know it today, was established in the 4th century CE, incorporating a more refined system of leap years and month lengths.
Tips for Navigating the Jewish Calendar
1. Utilize online resources: Numerous websites and mobile applications offer comprehensive information about the Jewish calendar, including dates, observances, and conversion tools.
2. Consult with a rabbi or Jewish community leader: For specific questions or guidance on navigating the Jewish calendar, consult with a rabbi or other knowledgeable member of your local Jewish community.
3. Explore Jewish literature and resources: Books, articles, and online resources provide valuable insights into the history, traditions, and significance of the Jewish calendar.
4. Engage in cultural immersion: Participating in Jewish cultural events and observing Jewish holidays can provide firsthand experience with the Jewish calendar and its impact on daily life.
5. Embrace the diversity of timekeeping: Recognizing and appreciating the differences between the Gregorian and Jewish calendars fosters a greater understanding of cultural diversity and the various ways humans have structured their understanding of time.
Conclusion: Bridging the Gap
The Gregorian and Jewish calendars, while distinct in their structure and underlying principles, offer valuable perspectives on the human experience of time. The Gregorian calendar, with its solar focus, provides a framework for global communication and coordination. The Jewish calendar, rooted in lunar-solar principles, reflects the rich tapestry of Jewish tradition and cultural identity.
By understanding the differences between these two systems, we gain a deeper appreciation for the diverse ways humans have structured their understanding of time and its impact on their lives. This knowledge fosters cultural understanding, promotes interfaith dialogue, and enriches our appreciation of the complex and multifaceted nature of human civilization.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Differences: A Comprehensive Guide to the Jewish and Gregorian Calendars. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!